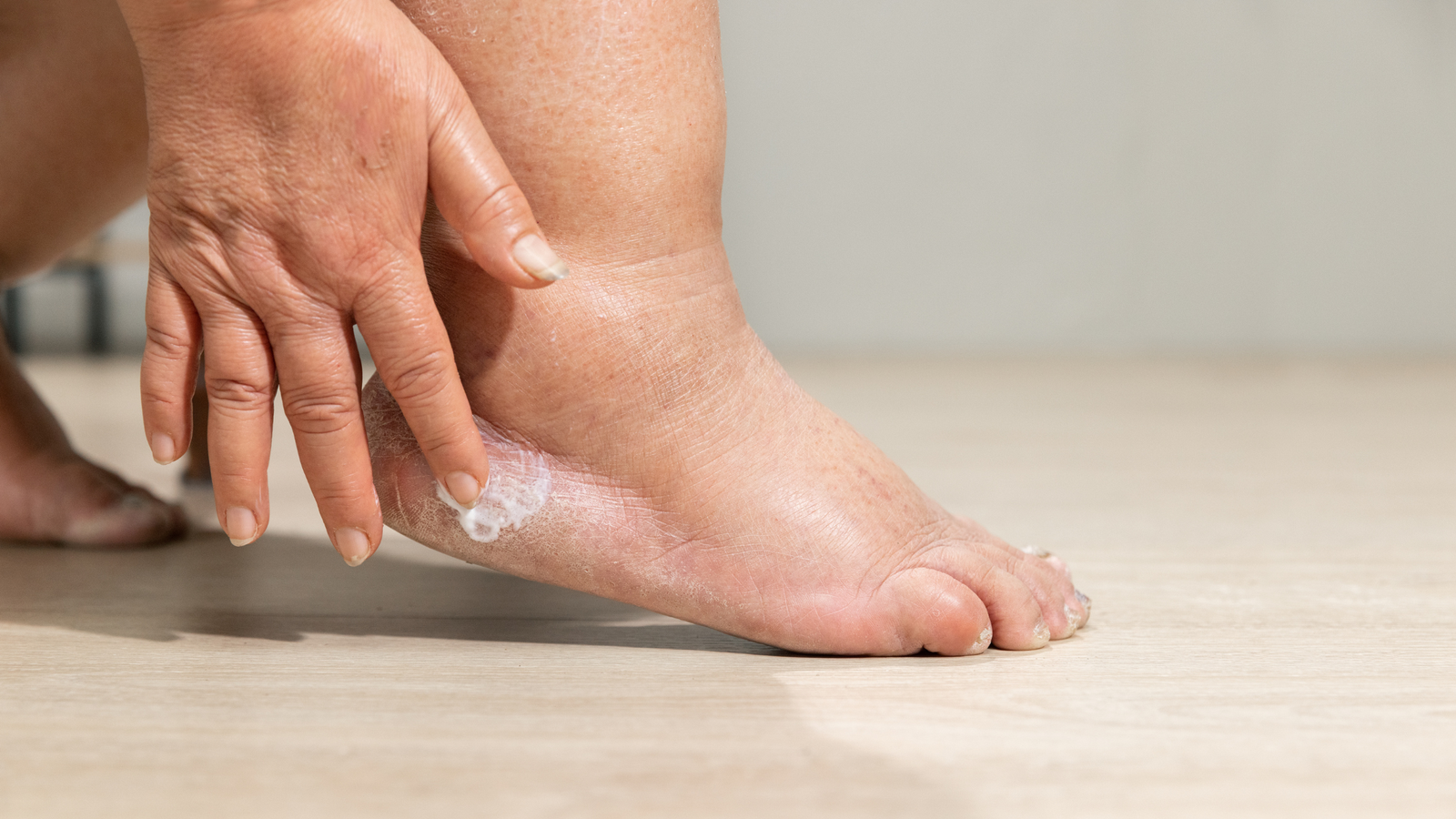
Edema, characterized by swelling in the lower legs and feet, is a common condition that can be caused by various factors. While many people rely on medications to alleviate the symptoms, addressing the underlying causes is crucial for long-term relief. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes of edema, including common and rare factors, and discuss effective strategies to manage and prevent edema naturally.

Sugar and High Carb Diet: The Double-Edged Sword
- How excessive sugar consumption leads to water retention and potassium deficiency
- The role of glycogen and its connection to fluid retention
- The impact of refined sugars on B1 deficiency and subsequent edema
- The potential benefits of adopting a low-carb, ketogenic diet
Sodium and Potassium Balance: The Key to Fluid Regulation
- The importance of maintaining a balance between sodium and potassium
- How consuming excess sodium without sufficient potassium can lead to fluid retention
- Strategies to increase potassium intake, including consuming potassium-rich vegetables and electrolyte supplements
- The impact of MSG and its role in fluid retention
Protein Deficiency, Liver, and Kidney Damage
- Understanding the connection between low protein levels in the blood and edema
- How liver damage affects protein production and contributes to fluid retention
- The role of kidney damage in protein loss and subsequent fluid accumulation
- Potential dietary and natural remedies to support liver and kidney health
Heart Problems and Edema
- Exploring the relationship between heart disease and fluid retention
- Understanding how congestive heart failure can lead to edema
- Natural approaches to support heart health and reduce edema symptoms
Thyroid Disorders and Edema
- The connection between hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism with fluid retention
- The concept of mixed edema and its impact on tissue puffiness
- Managing thyroid-related edema through proper diagnosis and treatment
Lipedema: Abnormal Fat Accumulation
- Understanding the hormonal and genetic factors associated with lipedema
- Exploring the impact of estrogen on fat distribution
- The potential benefits of a low-carb, higher fat diet in managing lipedema symptoms
Medication Side Effects and Edema
- Recognizing common medications that can cause edema
- Discussing the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional for medication adjustments
- Exploring alternative herbal options with fewer side effects
- The role of milk thistle in protecting the liver from medication-related complications
Lymphedema: Challenges and Management
- Understanding the nature of lymphedema and its impact on the lymphatic system
- Exploring therapeutic options such as manual lymphatic drainage and compression garments
- The potential benefits of low-level laser therapy and regular exercise in managing lymphedema
Edema in the lower legs and feet can arise from various causes, including dietary factors, organ damage, hormonal imbalances, and medication side effects. By addressing the underlying causes and adopting targeted approaches, such as dietary modifications, natural remedies, and lifestyle changes, individuals can effectively manage and prevent edema. It is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis, treatment, and guidance on the most suitable strategies for each specific case.
FAQs
1. What is edema?
Edema is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the body’s tissues, leading to swelling. It most commonly affects the lower legs and feet but can occur anywhere in the body.
2. What are the common symptoms of edema in the lower legs and feet?
The common symptoms include swelling, puffiness, stretched or shiny skin, and skin that retains a dimple after being pressed for several seconds.
3. Can lifestyle changes and natural remedies help in managing edema?
Yes, lifestyle changes and natural remedies can play a significant role in managing edema. This includes dietary modifications, such as reducing salt and sugar intake, increasing consumption of potassium-rich foods, regular exercise, and ensuring adequate protein intake.
4. How does excessive sugar consumption contribute to edema?
Excessive sugar consumption can lead to water retention and potassium deficiency. The body stores glucose as glycogen, which binds with water and can lead to fluid retention. High sugar intake can also deplete vitamin B1, contributing to edema.
5. What is the connection between a high-carb diet and fluid retention?
A high-carb diet can lead to increased glycogen storage in the body. For every gram of glycogen stored, the body retains approximately 3 grams of water, which can cause fluid retention and edema.
6. Why is the balance between sodium and potassium crucial for preventing fluid retention?
Sodium and potassium are essential electrolytes that help regulate fluid balance in the body. Consuming too much sodium or too little potassium can disrupt this balance, leading to fluid retention and edema.
7. What are some potassium-rich foods that can help manage edema?
Potassium-rich foods include bananas, oranges, apricots, spinach, sweet potatoes, mushrooms, peas, cucumbers, and zucchini.
8. How can low protein levels in the blood lead to edema?
Protein helps to keep fluid in the bloodstream, and low levels can cause fluid to leak out into the tissues, causing swelling.
9. What role does liver damage play in fluid retention?
Liver damage can impair the production of proteins like albumin, which are necessary to maintain blood volume and pressure. Reduced albumin levels can lead to fluid leakage from the blood vessels, causing edema.
10. Can kidney damage cause edema, and how?
Kidney damage can result in a loss of protein through the urine and reduced removal of excess fluid from the body, leading to edema.
11. What is the relationship between heart disease and edema?
Heart disease, especially congestive heart failure, can reduce the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup in the extremities and causing edema.
12. Can thyroid disorders contribute to edema?
Yes, both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can cause changes in the body that lead to fluid retention and edema.
13. What medications are known to cause edema?
Certain medications, such as calcium channel blockers, steroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and some diabetes medications, are known to cause edema.
14. Are there herbal alternatives that can be used to manage edema?
Some herbal remedies, such as dandelion, ginger, and hawthorn, may help manage edema. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying these remedies, as they may interact with other medications.
15. What are some effective therapies for managing lymphedema?
Effective therapies for lymphedema include manual lymphatic drainage, compression garments, exercise to encourage fluid drainage, and in some cases, low-level laser therapy.
References:
- Microbiological, pathological and microelement analyses in vicuñas affected with “dandruff”
- ANÁLISIS MICROBIOLÓGICO, PATOLÓGICO Y DETERMINACIONES DE MICROELEMENTOS EN VICUÑAS AFECTADAS CON “CASPA” MICROBIOLOGICAL, PATHOLOGICAL AND MICROELEMENT A NALYSES IN V ICUÑAS AFFECTED WITH “DANDRUFF”
- SOME MEDICAL ASPECTS OF THE POST‐OPERATIVE: STATE
- A CLINICAL STUDY TO EVALUATE THE EFFICACY OF THE MANAGEMENT OF DARUNAKA W.S.R. TO DANDRUFF AND SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS
- Studies get to root of dandruff, reveal new causes, cures for ailment